What are the Data types in Python ? And Difference between List, Tuple and set.
Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language that is easy to learn and widely used for web development, data analysis, artificial intelligence, and scientific computing. Python supports several data types:
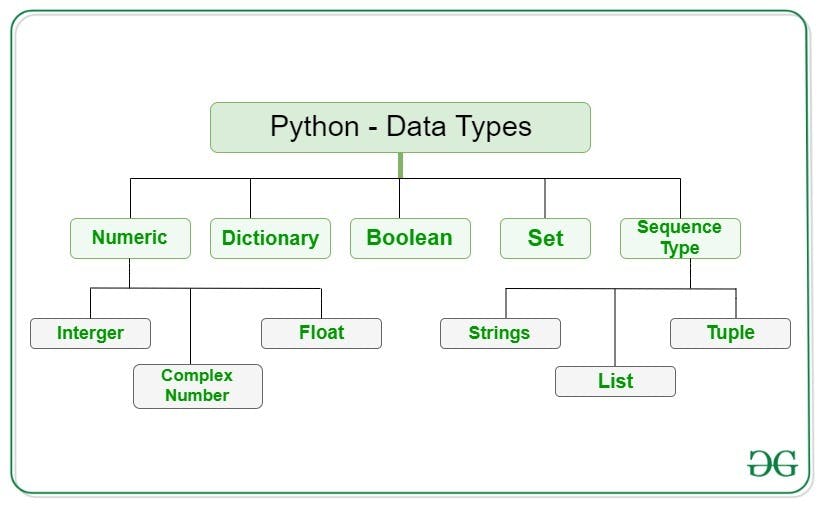
Numbers: Python supports integer, float, and complex numbers.
Strings: Strings are sequences of characters, enclosed in either single or double quotes.
Booleans: Booleans are True or False values that are used to represent logical values.
Lists: Lists are ordered sequences of values, enclosed in square brackets. Lists can contain any type of data, including other lists.
Tuples: Tuples are ordered sequences of values, enclosed in parentheses. Unlike lists, tuples are immutable, which means their values cannot be changed once they are created.
Sets: Sets are unordered collections of unique values, enclosed in curly braces. Sets are useful for performing mathematical operations such as union, intersection, and difference.
Dictionaries: Dictionaries are unordered collections of key-value pairs, enclosed in curly braces. Dictionaries are used to store data in a way that can be easily accessed and manipulated using the keys.
Python also supports some advanced data types such as arrays, deque, namedtuples, and more. Each data type has its own set of methods and operations that can be used to manipulate and perform calculations on the data.
Difference between List, Tuple and Set -
List, tuple, and set are three different types of data structures in Python. The main differences between them are:
List:
Lists are mutable, meaning you can change their contents after they are created. Lists are ordered, meaning the elements in a list have a specific order, and you can access them by their index. Lists can contain duplicate elements. Lists are created using square brackets [].
Tuple:
Tuples are immutable, meaning you cannot change their contents after they are created. Tuples are ordered, meaning the elements in a tuple have a specific order, and you can access them by their index. Tuples can contain duplicate elements. Tuples are created using parentheses () or the tuple() function.
Set:
Sets are mutable, meaning you can change their contents after they are created. Sets are unordered, meaning the elements in a set have no specific order, and you cannot access them by their index. Sets cannot contain duplicate elements. Sets are created using curly braces {} or the set() function. In summary, lists are ordered and can contain duplicate elements, tuples are ordered and cannot contain duplicate elements, and sets are unordered and cannot contain duplicate elements.

