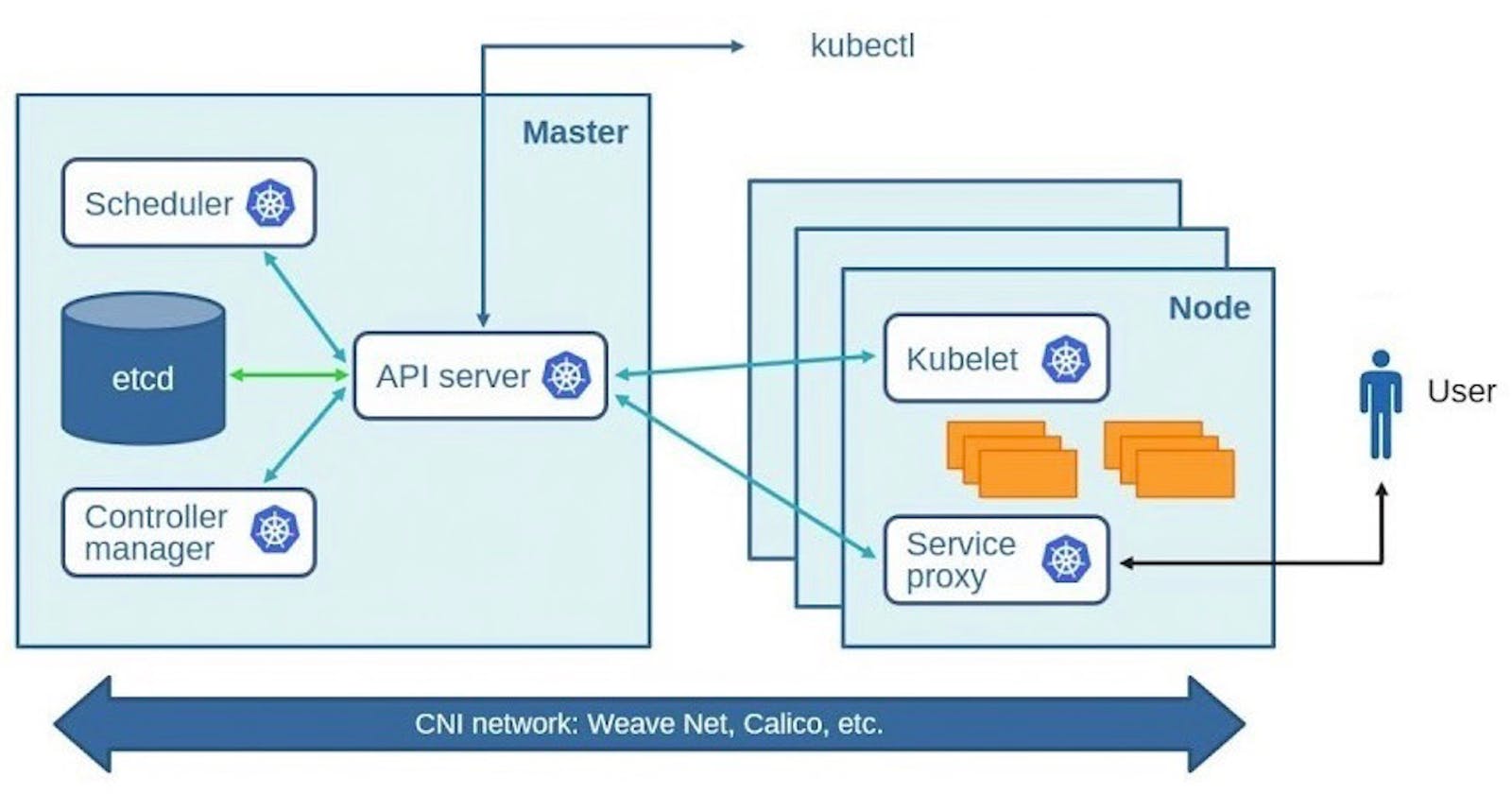
Kubernetes is an open-source platform that is used to deploy, scale, and manage containerized applications. It was originally developed by Google and is now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). Kubernetes provides a way to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications across a cluster of nodes.
The architecture of Kubernetes is based on a master-slave model. The master node is responsible for managing the overall state of the cluster and the individual worker nodes, also known as minion nodes, are responsible for running the containerized applications.
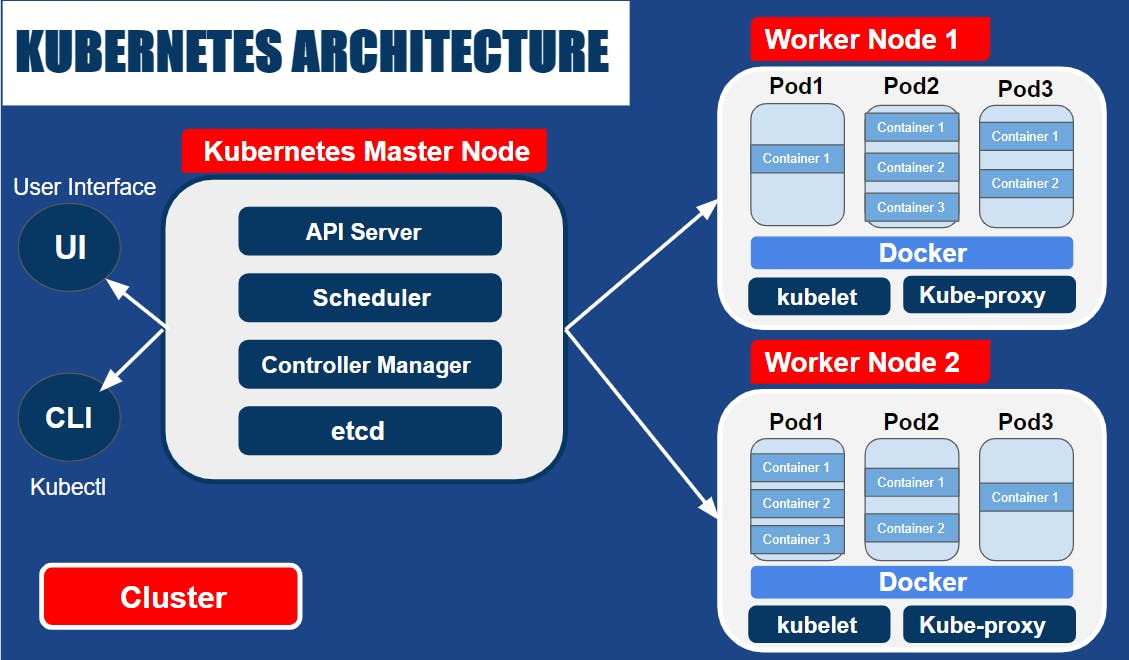
The main components of the Kubernetes architecture are:
Master Node: The master node is the brain of the Kubernetes cluster. It manages the overall state of the cluster and makes decisions on where to schedule applications, which nodes to use, and how to scale the applications. The master node consists of several components including the API server, etcd, kube-scheduler, and kube-controller-manager.
API Server: The API server is the front end of the Kubernetes control plane. It exposes the Kubernetes API, which is used to manage the cluster and its resources.
etcd: etcd is a distributed key-value store that is used to store the configuration data of the Kubernetes cluster.
kube-scheduler: The kube-scheduler is responsible for scheduling the containerized applications to run on the worker nodes based on available resources and other constraints.
kube-controller-manager: The kube-controller-manager is responsible for managing the various controllers that are used to maintain the desired state of the cluster.
Worker Node: The worker node is responsible for running the containerized applications. Each worker node has a kubelet that communicates with the API server to receive instructions on which applications to run and how to manage them. It also has a container runtime, such as Docker or container-d, to run the containers.
Pods: Pods are the smallest deployable units in Kubernetes. A pod is a logical host for one or more containers and includes shared storage, network, and other resources that are required to run the containers.
Service: A service provides a stable IP address and DNS name for a set of pods. This enables other applications within the cluster to communicate with the pods using a consistent address, even as the pods are added or removed from the cluster.
Ingress: An Ingress is an API object that manages external access to the services in a cluster. It provides a way to configure routing rules for incoming traffic and can be used to implement features such as load balancing, SSL termination, and name-based virtual hosting.
Overall, the architecture of Kubernetes is designed to provide a scalable and reliable platform for deploying and managing containerized applications in a distributed environment.